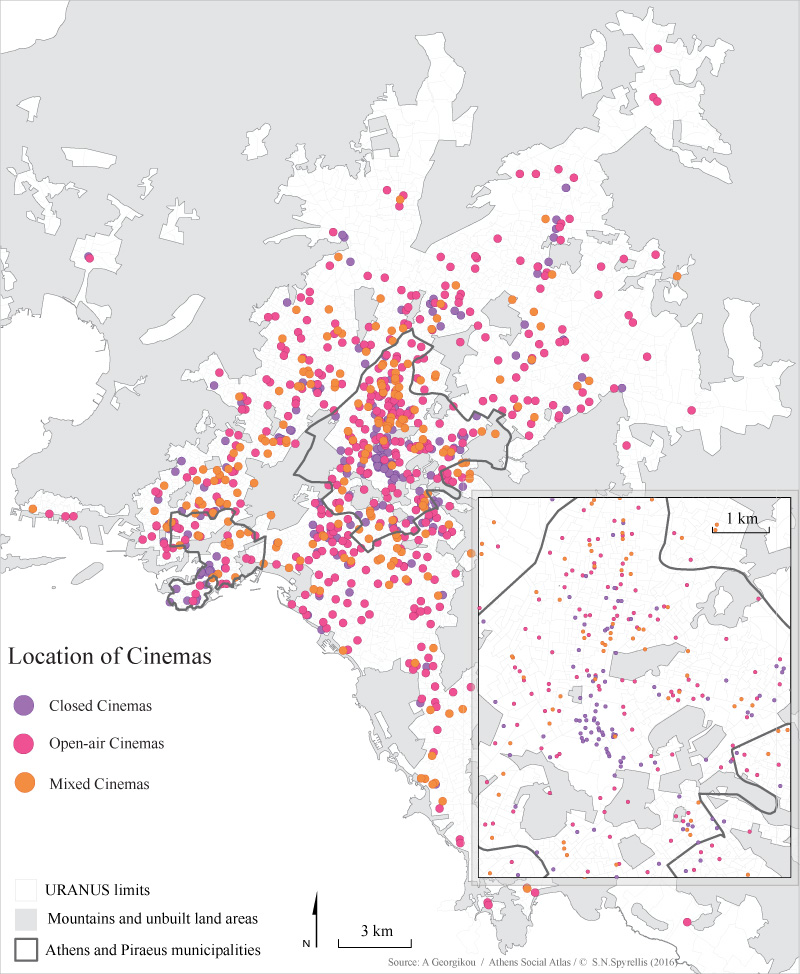
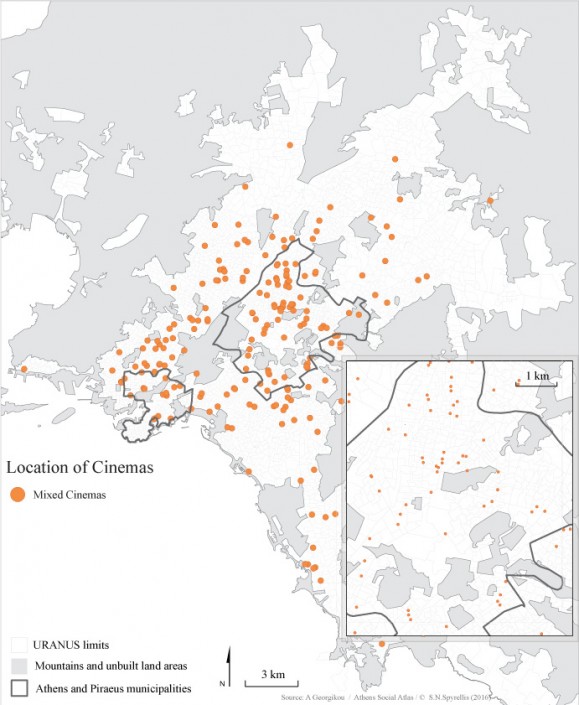
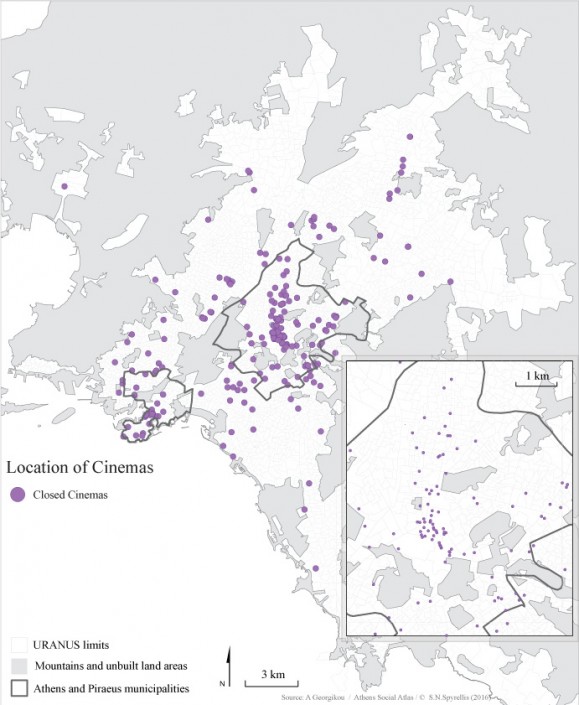
Changing number and location of cinemas from 1950 to 2015
2015 | Dec
In its early form, cinema was a street show and film screenings took place in open spaces such as squares or coffee shop yards. The first specialist halls that exclusively hosted film screenings appeared in the beginning of the 20th century. They copied the theatre set-up and their design resembled the cinema theatres as we know them today. The screen was the main focus point and the remaining elements arranged opposite it.
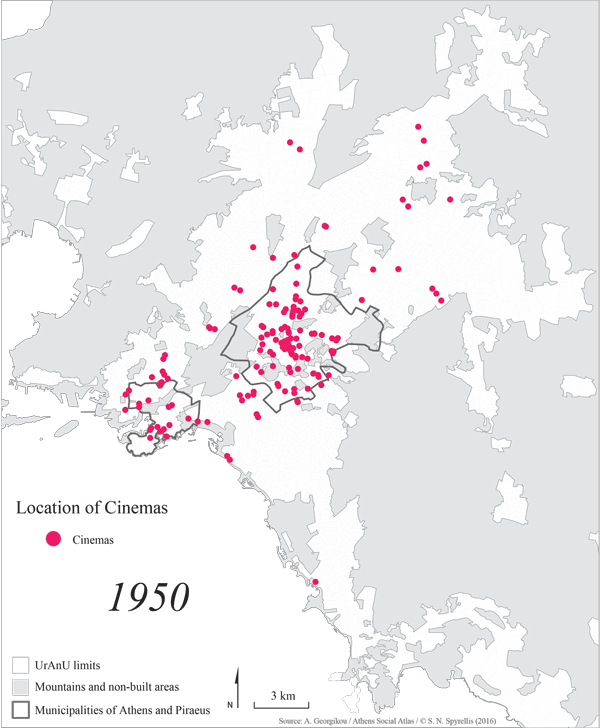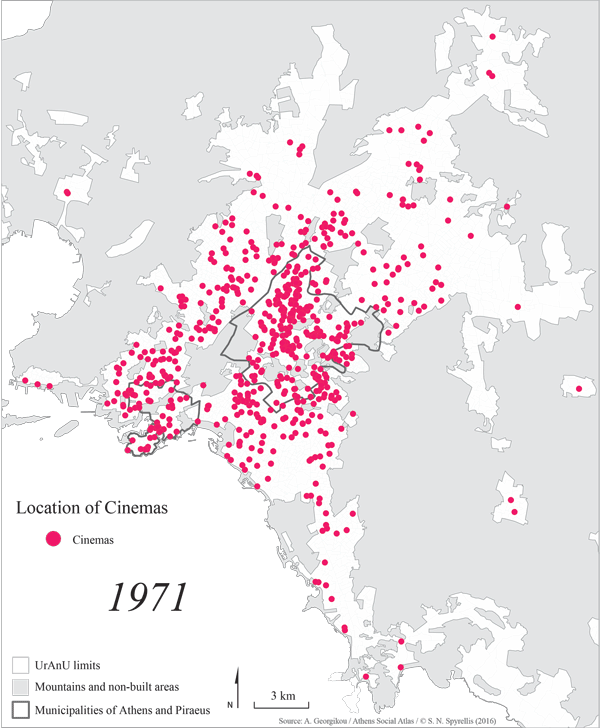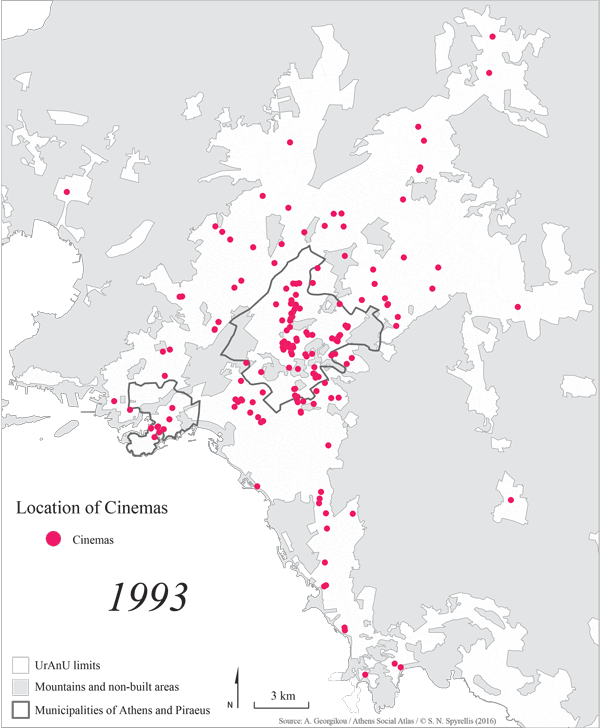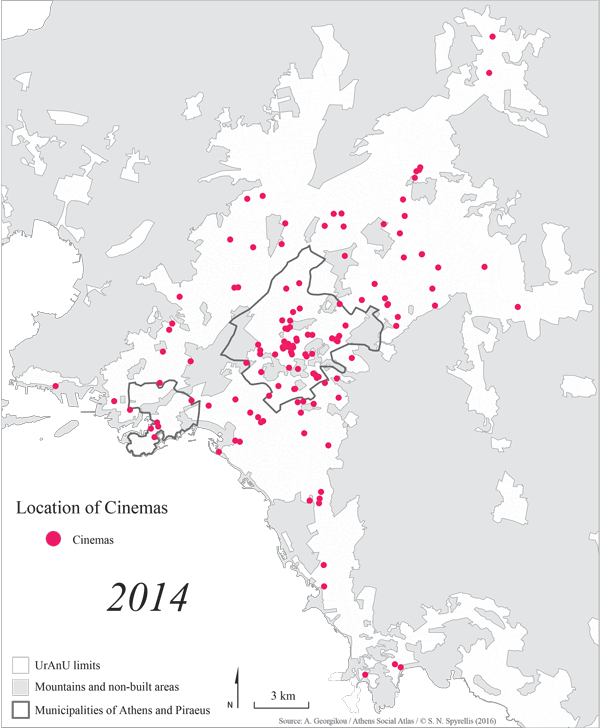
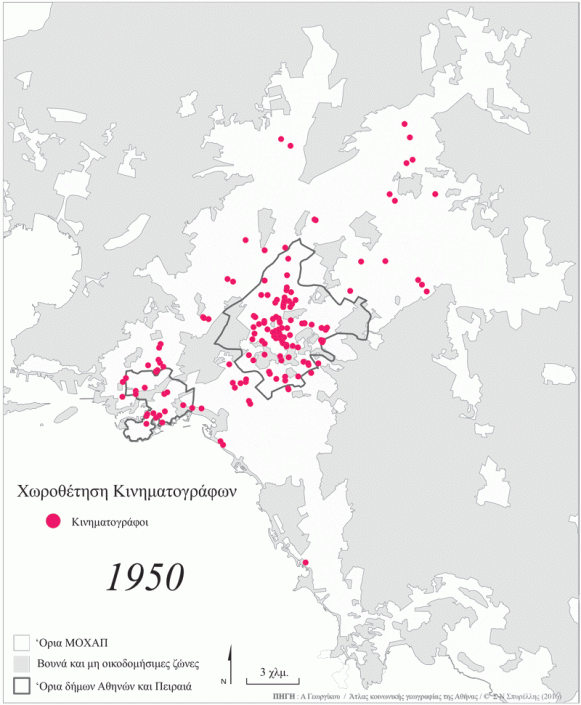
Cinema as a form of entertainment was established in Greece after the end of the second World War and the subsequent Greek civil war. The 1950s and 1960s were the heyday of cinema, in terms of film production while the construction of special venues also peaked during that period. In the 1950s film production ranged from 4 to 6 movies per annum but in the 1960s this number rose to 60 and peaked at 90 movies per annum in the early 1970s. The number of cinemas also increased, in order to accommodate the rapidly rising popularity of this new form of entertainment. Thus, while in 1950 Attica numbered 153 venues by 1969 their number had almost quintupled to reach 667.
In the 1950s, most cinema venues were located in the centre of Athens, in Piraeus and in the northern suburbs. These areas had high concentrations of venues in the 1960s too, although new cinemas were established throughout Attica during that decade. During this period, the great internal migration of population from the countryside to Athens caused new conurbations to emerge and increased the population of existing municipalities. The incoming population initially moved into the city centre (in the Municipality of Athens the population rose by approximately 50% in the 1960s) while during the 1970s the population of neighbouring and more distant municipalities increased significantly. Construction of new cinemas in almost every municipality went hand in hand with these population trends in response to growing demand for this new form of entertainment.
Map 1: Location of regular, open-air and mixed type of cinemas in the wider Athens area from 1950 to 2014.
Cinema venues can be categorised according to their geographical distribution and the class stratification of their clientelle. In particular there were five categories of venues during the post-war period and up to the 70s.
- premiere cinemas: included luxurious venues, were the first to screen new films and were mainly located in the city centre.
- second screening cinemas: they focused on older films and were both in the centre as well as the suburbs.
- working class cinemas: mainly located in areas with working class populations
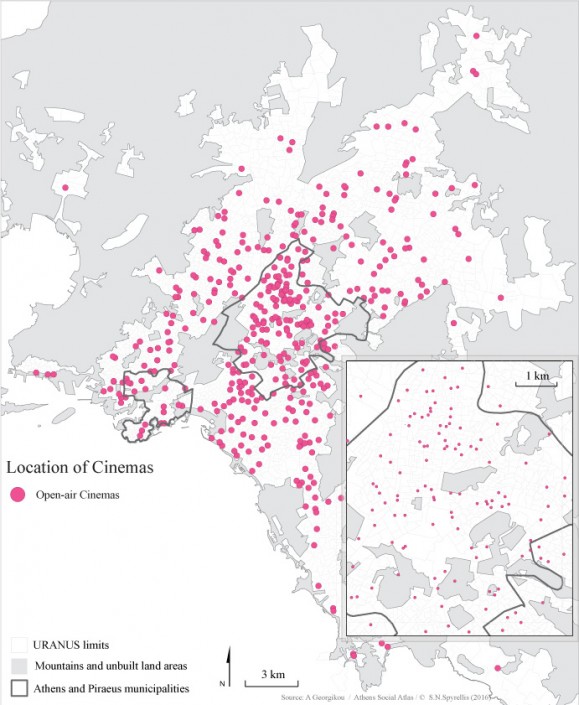
- open air cinemas: these were particularly popular throughout the post-war period. Open air cinemas were built all over Attica; in the centre, in the working class neighbourhoods and in the urban periphery.
- newsreel cinemas
Growth in the cinema and film-making industries continued apace until 1971, which marked a reversal of the trend for both venues and Greek film production. Film production dropped to 40 films a year, while the number of venues also started to decline. In 1970 there were 685 cinemas in Attica, the number dropped to 501 in 1975, while in 1979 only 414 were left. The main factors behind the crisis were the emergence of television and video, which became increasingly popular with viewers, keeping them away from cinemas. This change in consumer preferences was reflected in the number of tickets sold. There were128.5 million tickets sold in 1970 but only 48 million in 1975.
The downturn continued for another 25 years, until 2000. There were 402 theatres operating in 1980, about half that in 1990 (233 venues) and 205 were left in 1999. It is worth mentioning that although venue numbers were dropping, constant efforts were made to promote the cinematic product and new cinemas were built in a wide range of locations. Open air cinemas still were the most popular with Athenians as they were ideally suited to the climate, and they were often a functional element of urban neighbourhoods.
In contrast to every year since 1975 there were four more venues in 2000 compared to the year before. That decade marked the recovery of cinema, as witnessed by ticket sales: the number of tickets sold rose to 13 million in 2009, up from 8.5 million in 1998. This recovery is linked to a large extent to the delivery of the product in a different form, in multiplex venues (cinemas with two or more screens). The larger multiplex cinema in Athens has 20 halls. These spaces offer a wide selection of popular films and parallel activities addressed to various age groups, all under one roof. Following the example of large shopping centres, multiplexes are located on main streets that are well served by public transport . Besides, cimenas often serve as anchor facilities in large shopping malls.
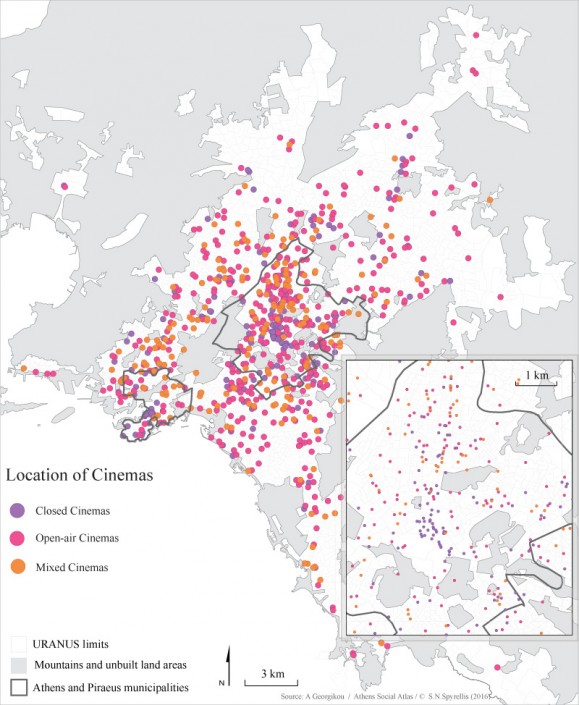
Map 2: The development of cinemas in the wider Athens area from 1950 to 2014.
Today, the construction of cinema venues has stopped. The last multiplex in Attica was built in 2012 and at present, only 151 screens operate, down from 164 in 2010 (52 in the centre, 14 in Piraeus and 24 in the northern suburbs). The changes in the location of cinema venues from 1950 to 2015 (map 2) indicates that supply followed the population of the city. This means that it responded to the explosive population growth as well as to the expansion of the periphery of Athens. – It also followed the international changes in the industry, which were an effort to survive the fierce competition from personalised home entertainment products.
Entry citation
Georgikou, A. (2015) Changing number and location of cinemas from 1950 to 2015, in Maloutas T., Spyrellis S. (eds) Athens Social Atlas. Digital compendium of texts and visual material. URL: https://www.athenssocialatlas.gr/en/article/cinemas/ , DOI: 10.17902/20971.7
Atlas citation
Maloutas T., Spyrellis S. (eds) (2015) Athens Social Atlas. Digital compendium of texts and visual material. URL: https://www.athenssocialatlas.gr/en/ , DOI: 10.17902/20971.9
References
- Θεοδοσίου Ν (2008) Οι πρώτες κινηματογραφικές αίθουσες. Μοτέρ 11: 53–59. Available from: https://www.academia.edu/3415425/οι_πρώτες_κινηματογραφικές_αίθουσες.
- Θεοδωράτος Μ (2005) Πολυκινηματογράφοι: το «βαρύ πυροβολικό» του κλάδου διασκέδασης και αναψυχής. Η Καθημερινή, Αθήνα, 10ο Σεπτέμβριος. Available from: http://www.kathimerini.gr/227831/article/oikonomia/ellhnikh-oikonomia/polykinhmatografoi-to-vary-pyrovoliko-toy-kladoy-diaskedashs-kai-anayyxhs.
- Κατσουνάκη Μ, Θεοδοσίου Ν, Χεκίμογλου Ε, κ.ά. (2001) Ιστορίες από τον Ελληνικό Κινηματογράφο. Επτά Ημέρες, Η Καθημερινή, Αθήνα, 11ο Νοέμβριος.
- Κεσίσογλου Β (2013) Μία συνοπτική Ιστορία του Κινηματογράφου. Αθήνα: Αιγόκερως.
- Κοκκίνη Ρίνκ Σ (2002) Τα πρώτα βήματα του ελληνικού κινηματογράφου. Ιστορία Εικονογραφημένη, Αθήνα. Available from: http://www.istoria.gr/may02/3.htm.
- Κολοβός Ν (1988) Κοινωνιολογία του Κινηματογράφου. Αθήνα: Αιγόκερως.
- Κουσουμίδης Μ (1981) Η ιστορία του Ελληνικού Κινηματογράφου. Αθήνα: Καστανιώτη.
- Ορφανουδάκης Δ (1998) Ο κινηματογράφος στην Ελλάδα. Ένας αιώνας αρχιτεκτονική του κινηματογράφου. Πειραιάς.
- Σηφάκη Ε (2012) Η κοινωνική εμπειρία της κινηματογραφικής αίθουσας : χωρικές πρακτικές και πολιτισμικές δομες. Στο: Σηφάκη Ε, Πούπου Ά, και Νικολαϊδου Α (επιμ.), Πόλη και κινηματογράφος : Θεωρητικές και μεθολογικές προσεγγίσεις, Αθήνα: Νήσος, σσ 135–163.
- Σολδάτος Γ (2002) Ιστορία του ελληνικού κινηματογράφου. Βενιανάκη Έ (επιμ.), Αθήνα: Αιγόκερως.
- Χριστόπουλος Γ και Χριστόπουλος Ι (2008) Εμφάνιση & Εξάπλωση των κινηματογραφικών αιθουσών στο δήμο της Αθήνας 1897-2000. Αθήνα. Available from: http://hg-lab.blogspot.gr/p/blog-page.html.
- Gardiakos S (2009) A Compilation of Greek Made Movie Projectors and other Cinematic Equipment. Aurora, Kalamata: Unigraphics. Available from: http://bioscope.biz/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/book_greek_made_movie_projectors.pdf.
- Thomson K and Bordwell D (2011) Ιστορία του κινηματογράφου. Μια εισαγωγή. Λέρος Ν, Κολαϊτη Ρ, and Στεφανή Ε (eds), Αθήνα: Πατάκης.
Online sources
- http://www.athinorama.gr/
- http://bill-files.blogspot.gr/2014/01/8.html
- http://bioscope.biz/resources/book_greek_made_movie_projectors.PDF
- http://cineanamnisi.blogspot.gr/
- http://www.earlycinema.com/
- http://www.eie.gr/archaeologia/gr/arxeio_more.aspx?id=195
- http://www.ekke.gr/estia/gr_pages/gr_cinema/Cinema99/Cinemahtm#_Toc536584943
- http://www.istoria.gr/may02/3.htm
- http://www.kathimerini.gr/227831/article/oikonomia/ellhnikh-oikonomia/polykinhmatografoi-to-vary-pyrovoliko-toy-kladoy-diaskedashs-kai-anayyxhs
- https://paliasinema.wordpress.com/kinimatografo/
- http://projects.pblogs.gr/h-istoria-toy-kinhmatografoy-omada-1.html